Difference between revisions of "Kitsch"
(→Maori Rock Art) |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
{{wikipedia|Kitsch}} | {{wikipedia|Kitsch}} | ||
| − | Archaeological items of iconic status become the subject of modern copies and re-use of the imagery. New Zealand items are not immune. | + | Archaeological items of iconic status can become the subject of modern copies and re-use of the imagery. New Zealand items are not immune. |
Revision as of 13:40, 18 January 2014
Contents
Archaeological Kitsch
Archaeological items of iconic status can become the subject of modern copies and re-use of the imagery. New Zealand items are not immune.
Maori Rock Art
|
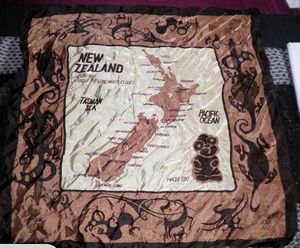
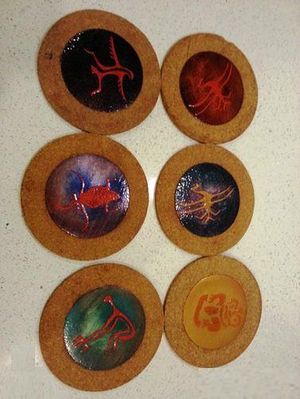
Rock drawings seem to have been particularly prone to this - borrowings appearing on fabrics, glassware, ceramics, postage stamps and even matchboxes. O'Regan discusses this use in the context of cultural property[1]. |
| Scarves | |||
| Glasses | |||
| Enamelled Dishes | |||
| Stamps | |||
| Fabric / Carpet | |||
 Rock art used on fabric. This was produced by blockprinting by poet Rex Fairburn. He obtained the artwork for this from Theo Schoon and reproduced using linocut blocks. Wikipedia has an article on Schoon. Another print can be seen here. Fairburn and Schoon have Dictionary of New Zealand Biography entries. |
|||
| Ceramics | |||
| Matchboxes | |||
| ; | |||
| Furniture | |||
| Wall Decorations Enamelled | |||
| Wall Decorations Copper | |||
| Wall Decorations Wood | |||
| Clothing | |||
| Jewellery | |||
Maori Other
Colonial
|
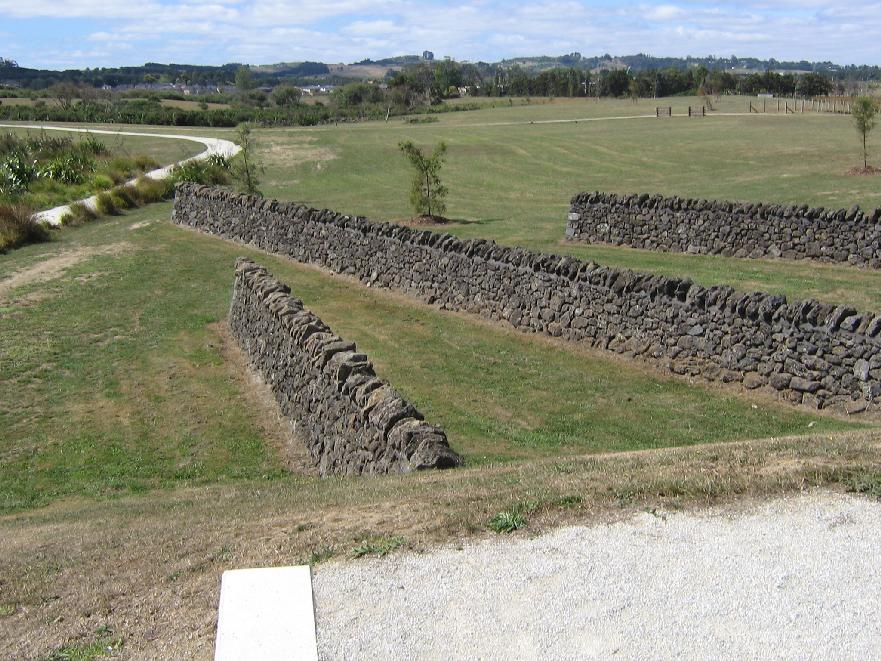
Barry Curtis Park in South Auckland has volcanic rock walls, reconstructed from a nearby farm site. The unfortunate result is what happens when landscape architecture captures archaeological reconstruction.
|
Not Quite Archaeological

An execrable souvenir of the 1940 Centennial Exhibition. A Birmingham made badge representing the Hinemoa and Tutanekai gateway at the Model Pa, Whakarewarewa. It doesn't include a kiwi! This sold for $113.99 on Trademe so its awfullness was certainly appreciated.The gateway itself is an example of bowdlerisation of Maori carving.
References
- ↑ O'Regan, G. 2008 The shifting place of Ngai Tahu rock art. in Sue O'Connor, Geoffrey Clark, Foss Leach (Eds), Islands of inquiry : colonisation, seafaring and the archaeology of maritime landscapes. Terra Australis 29 Accessed at http://epress.anu.edu.au/terra_australis/ta29/pdf/ch26.pdf