Difference between revisions of "Pa"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
A ''pa'' [pronounced: pah] is a Maori hill-fort dating from the 17th to 19th centuries. Built on hillsides or promontories, these fortifications were defined by their use of palisades, earthen banks, and ditches, and were most often built on coastal headlands. Cook, the first westerner to view a Pa, remarked that “the best engineer in Europe could not have chose a better [site] for a small number of men to defend themselves against a greater.” [2 36] Despite their defensible position, however, pa were often left unattended in order for the residents to farm food in the surrounding areas. | A ''pa'' [pronounced: pah] is a Maori hill-fort dating from the 17th to 19th centuries. Built on hillsides or promontories, these fortifications were defined by their use of palisades, earthen banks, and ditches, and were most often built on coastal headlands. Cook, the first westerner to view a Pa, remarked that “the best engineer in Europe could not have chose a better [site] for a small number of men to defend themselves against a greater.” [2 36] Despite their defensible position, however, pa were often left unattended in order for the residents to farm food in the surrounding areas. | ||
| − | [[Image:Model_Of_Maori_Pa_On_Headland.jpg]] | + | [[Image:Model_Of_Maori_Pa_On_Headland.jpg|thumb|right|Model of Maori Pa]] |
== Pa Classification and Defense == | == Pa Classification and Defense == | ||
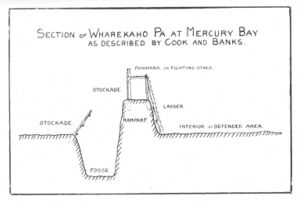
| − | [[Image:Bes02Maor315a.jpg]] | + | [[Image:Bes02Maor315a.jpg|thumb|right|Diagram of Pa Fortifications]] |
Pa were classified into three classes by Les Groube in 1969 according to the level of fortification applied to the site. While some sites were simply terraced beyond the palisade, others utilized ditches, banks, trench moats, and even a puwhara, or ‘fighting stage,’ built along the back of the palisade. The classes of palisade, according to Les Groube, were as follows; | Pa were classified into three classes by Les Groube in 1969 according to the level of fortification applied to the site. While some sites were simply terraced beyond the palisade, others utilized ditches, banks, trench moats, and even a puwhara, or ‘fighting stage,’ built along the back of the palisade. The classes of palisade, according to Les Groube, were as follows; | ||
Revision as of 22:57, 22 February 2010
A pa [pronounced: pah] is a Maori hill-fort dating from the 17th to 19th centuries. Built on hillsides or promontories, these fortifications were defined by their use of palisades, earthen banks, and ditches, and were most often built on coastal headlands. Cook, the first westerner to view a Pa, remarked that “the best engineer in Europe could not have chose a better [site] for a small number of men to defend themselves against a greater.” [2 36] Despite their defensible position, however, pa were often left unattended in order for the residents to farm food in the surrounding areas.
Pa Classification and Defense
Pa were classified into three classes by Les Groube in 1969 according to the level of fortification applied to the site. While some sites were simply terraced beyond the palisade, others utilized ditches, banks, trench moats, and even a puwhara, or ‘fighting stage,’ built along the back of the palisade. The classes of palisade, according to Les Groube, were as follows;
Class I – Terraces only. Class II – Sites with banks and transverse ditches. Class III – Sites with both transverse and lateral ditches and banks, as well as moated sites.
These fortifications could be erected quickly, and proved highly effective against even the most advanced foes, most notably the British Empire, who had limited success against the earthen fortifications of the Pa, which could in some way be considered the birthplace of trench warfare, as even firearms were unable to penetrate the packed defenses.
Fort Interior
Withing the fortifications of the pa, there was generally some sort of dwelling area (with the exception of some built for the sole purpose of quick defense). Included would be houses of varying style and size, but consisting largely of rectangular architecture with pitched, wide-eaved, roofs. Outside of these houses were outdoor cooking areas, with some pa having outdoor sheds/awnings in which meals were taken. In addition to the dwellings, found within the sites of these forts are numerous storage areas. These areas took up a large part of the interior space, and in order to prevent animals from from getting to supplies were built as raised lofts. In some instances, the storage area would take the form of a large pit with raised edges.
Some Notable Sites
Tiromoana pa, Te Awanga, Hawke's Bay
Manuaitu pa, Apetea, Waikato
Taniwha pa, Te Kauwhata
Paroa pa, Bay of Islands
References
Fox, Aileen. Prehistoric Maori Fortifications. New Zealand, Longman Paul Limited, 1976
Best, Elsdon. The Pa Maori. New Zealand, A. R. Shearer Government Printer, 1975
Best, Elsdon. The Maori - Volume II. New Zealand, Polynesian Society, 1941. (New Zealand Electronic Text Centre http://www.nzetc.org/etexts/Bes02Maor/Bes02Maor308a.jpg)